How is RFID used in the logistics field?
How is RFID used in the logistics field?
Application of RFID in logistics field
Job task requirements: Understand the concepts and principles of RFID technology, analyze the advantages and disadvantages of RFID technology, understand the types of RFID, and be familiar with common applications of RFID.
Radio frequency identification technology (RFID) is a non-contact automatic identification technology that entered the practical stage in the mid-20th century. The radio frequency identification system consists of radio frequency tags and readers. Radio frequency tags are carriers that carry identification information, and readers are devices that obtain information. Radio frequency identification tags and readers use induction, radio waves or microwaves to conduct two-way communication to realize the identification and data exchange of information stored in the tags.
1. Principle of RFID
The RFID technology system consists of three parts: electronic tag, reader, antenna and host system. The electronic label is equivalent to the barcode in current barcode technology, which stores the unique identification code of the goods, including key supply information such as origin and date. Different from barcodes, labels can store a large amount of information and can send cargo information in the form of wireless signals automatically or under the action of external forces. The sending distance is related to the type of electronic tag, ranging from tens of centimeters to tens of meters, achieving non-contact operation. The reader is a wireless signal receiving device, and its complexity varies greatly depending on the electronic tag. After the reader receives the information sent by the tag, it translates and verifies it. After determining that it is correct, it instructs the transmitter to stop working, so that multiple tags can be read in a short time and in a small space, and cargo information can be obtained in batches. The transmission and reception of data transmitted between the electronic tag and the reader is completed by the antenna, and the host system is responsible for processing these data movements.
The basic principle of RFID technology is electromagnetic theory. The advantage of the radio frequency system is that it is not limited to line of sight, and the recognition distance is farther than that of the optical system. Radio frequency identification tags have the ability to be read and written without contact, can carry a large amount of data, are difficult to forge, and are intelligent.
Radio frequency identification technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology. The antenna emits radio waves to form a magnetic field. After the electronic tag enters the magnetic field, the coil inside it can induce the magnetic field and generate current. Under the energy supply of current, the stored product information is converted into radio frequency signals and sent to the reader. After the reader reads and decodes the information, it is sent to the host system through the antenna for relevant data processing.
The tag in RFID is a combination of RFID tag chip and tag antenna. When used as shown in the figure, special information is first encoded into the electronic tag, and then the tag is affixed to the items that need to be identified or tracked.
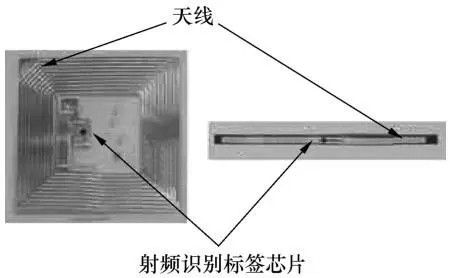
Some RFID systems are read-only, others allow adding or changing existing information in the tag. All RFID systems feature contactless reading capabilities at reading distances from 2.54 cm to 254 cm or greater. Since harsh environments may cause damage or malfunction to contact or near-contact readers, the application of non-contact readers will be very wide, especially some radio frequency identification systems already have a memory of up to 1M , which brings great convenience to data processing.
Knowledge link: Factors affecting radio frequency identification systems
The radio frequency identification system is non-contact reading and writing, and its wireless transmission distance is determined by many factors, such as transmission frequency antenna design. For the specific situation of applying radio frequency identification technology, the transmission distance, operating frequency, data capacity, size, weight, positioning, response speed and selection ability of the tag should be considered.
2. Characteristics of RFID
(1) Radio frequency identification tags are resistant to harsh environments, waterproof, antimagnetic, high temperature resistant, have a long service life, and are more flexible in placement than barcode tags. And it requires almost no maintenance. Dust, paint and other opaque substances will not affect the readability of RF tags.
(2) RFID tags are non-contact reading and do not need to be read like barcode tags. The information will not be washed away by strong magnetic fields. Information can be read accurately as long as it is placed within the electromagnetic field formed by the reading device, with an extremely low error rate. . Therefore, it is more suitable for use with various automated processing equipment, while reducing or even eliminating the waste of human resources, reduced efficiency, errors and error correction costs caused by manual intervention in data collection.
(3) RFID can perform thousands of reads per second and can process many tags at the same time. It is efficient and highly accurate, allowing companies to operate without reducing (or even improving) efficiency. Without increasing (or even reducing) management costs, it can greatly improve the precision of management, make the entire operation process transparent in real time, and create huge economic benefits.
(4) The data on the RFID tag can be modified repeatedly, which can not only be used to transmit some key data, but also enable the RFID tag to be recycled and reused within the enterprise. Convert one-time costs into long-term amortized costs, further saving enterprise operating costs while reducing the risk costs of enterprises adopting RFID technology
(5) The reading of RFID tags does not require visual visibility because it does not rely on visible light, so it can be used in harsh environments that barcode technology cannot adapt to. Such as high dust pollution, outdoors, etc., which can further expand the application scope of radio frequency identification technology.
(6) The radio frequency identification system can also identify fast-moving items. Items with radio frequency tags do not need to be stationary during the reading process.
(7) RFID tags have strong confidentiality and high security. RFID chips are very difficult to counterfeit. Hackers would need a deep understanding of wireless engineering, coding algorithms, and decryption techniques to crack it. In addition, hierarchical confidentiality measures can be implemented on the data on the label, so that the data can be read at certain points in the supply chain but not at other points. Some RFID standards also specify additional security measures.
Radio frequency identification technology is applicable to a wide range of fields, such as material tracking, vehicle and shelf identification, transportation identification, road and bridge toll collection, security access control, tracking, automatic guidance of cars, automatic storage, tool identification, personnel monitoring, parcels and baggage classification, vehicle monitoring, etc.
3. Types of RFID tags
There are many types of RFID tags. Implantable tags are as small as a grain of rice, while larger tags used for long-distance communications (and even global positioning systems) are as big as a handheld telephone.
Tags are divided into active tags and passive tags according to their working modes. The active tag itself carries a battery to provide it with the energy required for reader communication; the passive tag uses inductive coupling or backscattering working mode, that is, it obtains energy from the electromagnetic field or electromagnetic wave emitted by the reader through the tag antenna to activate the chip and adjust The matching degree between the radio frequency identification tag chip and the tag antenna feeds back the information stored in the tag chip to the reader.
Electronic tags can be divided into low-frequency electronic tags, high-frequency electronic tags, ultra-high frequency electronic tags and microwave electronic tags according to different frequencies.
Electronic labels can be divided into credit card labels, linear labels, paper labels, glass tube labels, round labels and special-purpose special-shaped labels based on different packaging forms.
4. Common applications of RFID technology in the logistics field
At present, radio frequency identification technology is widely used at home and abroad in visitor control, store anti-theft systems, item and inventory tracking, automatic charging, tracking, manufacturing process management, intermodal container and air cargo tracking, etc. It is especially widely used in modern logistics management and military logistics support. Combining RFID technology with portable data terminals (PDTs) allows the collected useful data to be stored or transmitted to a management information system. Connected to an appropriate scanner it can be effectively used in many automatic identification applications. Radio frequency identification technology is now widely used in the following fields.
1. Automatic identification of vehicles
(1)Realizing automatic identification of train numbers has been a long-standing dream of railway people. After the advent of RFID technology, it quickly attracted attention from the railway sector. Judging from foreign practice, the North American Railroad Association approved the automatic train number identification standard using RFID technology in early 1992. As of December 1995, 150,000 trains in North America had used it in three years. RFID devices were installed on trucks and 1,400 locations, successfully establishing an automatic vehicle number identification system in a large area for the first time. In addition, some European countries, such as Denmark and Sweden, have also established localized automatic vehicle number identification systems using RFID technology. Australia has also developed an automatic identification system in recent years for the identification and management of mining vehicles.
(2)Highway Toll Collection and Intelligent Transport System (ITS)
The automatic highway toll collection system is one of the most successful applications of RFID technology, which fully demonstrates the advantages of non-contact identification. The vehicle automatically completes toll payment while passing through the toll station at high speed, solving traffic bottlenecks and avoiding congestion. It also prevents problems such as embezzlement of tolls in cash settlement. American Amtch Company, Swedish Tagmaster Company, etc. have developed complete systems for highway toll collection.
(3) Contactless identification card
Most foreign transactions are completed using various cards, which are so-called non-cash settlements, such as phone cards, membership fee cards, savings cards, subway and bus passes, etc. In the past, most of these cards were magnetic cards or IC cards. Since magnetic cards and IC cards use contact reading, they have poor resistance to mechanical wear and interference from external strong electricity and magnetic fields, and magnetic cards are easy to forge. At present, there is a strong trend of being replaced by contactless identification cards. According to information provided by Japan's AIM, Japanese companies operating magnetic card phones plan to invest 500 million yen to replace the original magnetic card phones within two years starting in 2017; Japanese companies operating subways and game consoles have also invested A large amount of money was spent to cancel the original magnetic card equipment and replace it with contactless identification cards.
(4) Automation and process control of production lines
RFID technology is used to realize automatic control of production lines, monitor quality, improve production methods, and increase productivity, such as in automobile assembly lines. Many famous foreign cars, such as Mercedes-Benz and BMW, can be customized according to user requirements, which means that every car that comes off the assembly line is different. The assembly processes determined by tens of thousands of internal and external options are diverse, and it is difficult to handle such a complex task without a highly coordinated and complex control system. The German BMW company is equipped with an RFID system on its car assembly line to ensure that the car completes the assembly tasks accurately at each position on the assembly line, as shown in Figure
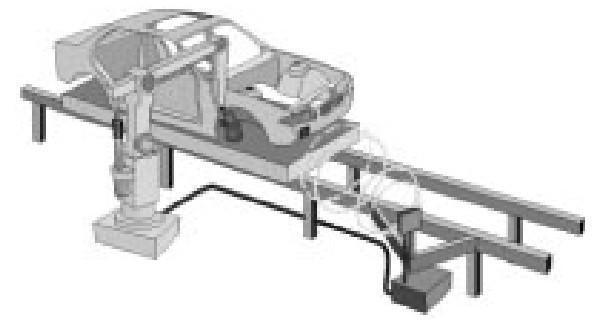
In industrial process control, many harsh and special environments have adopted RFID technology. Integrated circuit manufacturers such as MOTOROLA and SGSTHOMSON have adopted automatic identification process control systems incorporating RFID technology to meet the special requirements of semiconductor production for ultra-clean environments. Other automatic identification technologies, such as barcode technology, cannot work under such harsh chemical conditions and ultra-clean environments.
(5) Cargo tracking and item monitoring
The transportation of many goods requires accurate knowledge of the location of the goods, such as dangerous goods, etc. RFID equipment installed along the line can track the entire process of transportation, and some are also combined with GPS systems to implement effective tracking of goods. RFID technology is used in stores to prevent the theft of certain valuable items, such as Electronic Article Surveillance Systems EAS
Knowledge Link: Portable Data Terminal (PDT)
In recent years, there have been many applications of portable data terminals (PDTs), which can store or transmit useful data collected to a management information system. Portable data terminals generally include a scanner, a small but powerful computer with memory, a display and a keyboard for manual input. A resident memory operating system is installed in the read-only memory, which is used to control the collection and transmission of data. The data in the PDT memory can be transmitted to the host computer at any time through radio frequency communication technology. During operation, the location label is scanned first, and the shelf number and product quantity are entered into the PDT. This data is then wirelessly transmitted to the computer management system through RFID technology, and information such as customer product lists, invoices, shipping labels, product codes and quantities stored in the place can be obtained.
5. Application of RFID technology in e-commerce
E-commerce uses Internet technology to connect enterprises and customers. The entire supply chain consists of enterprises, logistics centers and customers, reducing intermediate links. Compared with traditional commerce, the role of logistics centers has become more and more prominent. Logistics centers are both corporate warehouses and customers' supply warehouses. The efficiency of the logistics center directly determines the efficiency of the entire supply chain. The use of RFID technology can improve the management level of the logistics center and effectively improve the speed of the e-commerce supply chain.
(1) Automatic warehousing operation
After receiving the incoming goods list, the warehouse of the logistics center begins acceptance and sorting. Before the goods are put into storage, it is necessary to pre-write the name, specification, manufacturer and other relevant data in the RFID electronic tag, and install the prepared label on the surface of the goods, packaging boxes or pallets. At the same time, the host system allocates cargo space to the batch of goods and generates warehousing instructions. A reader and a tablet computer are installed on the vehicle, and the warehousing instructions are sent to the tablet computer through the antenna from the host system. When getting on the forklift to pick up the goods, the reader on the truck reads the label information and compares it with the warehousing instructions on the tablet to ensure the correctness of the operation. A reader is also installed at the entrance of the warehouse door. When the goods are put into the warehouse, the reader automatically reads the goods information in batches, counts and records the time of entry, and sends the information to the host system. After the forklift reaches the target cargo location, the reader reads the cargo location label, confirms that it is consistent with the instructed target cargo location, puts the goods on the shelf, and sends a confirmation message to the host system. The host system confirms the warehousing and updates the database, and compares the final warehousing result with the purchase list. After confirmation, the warehousing work is completed.
Using wireless real-time transmission of RFID technology, various documents for warehousing operations are changed from manual entry to automatic reading. Realize paperless operations: Automatic verification through the host system reduces operational errors from the source and improves speed and accuracy. Of course, RFID tags can also be installed on each vehicle, and the host system can determine the location of the forklift at any time. When assigning warehousing tasks, select idle forklifts that are closer to the warehouse to increase the utilization rate of the forklifts. It can also record the workload of the forklift drivers and provide an objective basis for evaluating employee performance.
(2) Quick inventory
E-commerce logistics centers have larger warehouse areas and a larger number of storage locations. A tally clerk tallies a large number of storage locations every day, and it is difficult to remember the storage status of goods in each location. The inventory takes a long time and has a high error rate. In addition, traditional inventory work requires scanning barcodes and checking multiple times. After the goods are shipped, the barcodes on the goods will wear out, causing difficulties in subsequent work. RFID can well solve the problem of inventory
When entering the warehouse, the goods have been loaded with RFID tags. The tallyman holds a mobile reader. When walking through the shelves, the reader reads the goods information and transmits it to the host system in real time, completing the inventory of the goods in a short time. . Through RFID non-contact work, the inventory speed can be accelerated. The inventory verification time is 1/20 of the traditional barcode recognition time. At the same time, the re-inspection process is reduced and the problem of barcode wear is solved. The handheld reader can identify goods within a certain distance. Even if the goods are placed scattered, it will not affect the efficiency of inventory. Especially when the goods are placed in a higher position, it avoids the trouble of staff climbing up to take inventory.
(3) Efficient picking and outbound operations are highly efficient
E-commerce logistics faces personalized and diversified demands. The order volume of goods is large and the disassembly rate is very high. You even have to select a book or a bottle of medicine. Picking work is a key link in the logistics center, and its efficiency directly affects the efficiency of the entire center. The reason for the warehouse explosion problem that has arisen in the past two years is that the picking efficiency is too low, and the pickers are unable to cope with the sudden increase in picking workload, resulting in a serious backlog of goods. The application of RFID technology can increase picking speed and accuracy and significantly improve logistics efficiency.
When picking goods, the host system selects an idle forklift that is closer to the outbound area and sends outbound instructions to the forklift's tablet computer. After the forklift driver arrives at the target cargo location, the reader reads the cargo location label and cargo label, compares them with the outgoing instructions, and then takes away the goods after confirmation. The outbound door is also equipped with a reader. When all the goods are picked and pass through the warehouse door, the reader reads the cargo information, and the host system automatically enters the shipment quantity, product name, vehicle number and other information. Compare with the outbound order and change the data system if there is no error. If the quantity, variety, etc. do not match the outbound instructions, the host system will issue an alarm prompt command, usually with an LED light above the warehouse door. When the goods and other information are inconsistent with the outgoing instructions, this light will light up and a warning sound will sound to prompt the staff to review. The entire picking and shipping process is smooth and without pause, reducing the unboxing review and manual counting recording process of the traditional picking process, which is short in time and high in accuracy.

Navigation
News




